In order to check the accuracy and efficiency of the present method in the analysis of impact problems, a rectangular plate consisting of two different materials loaded by a sinusoidal impulsive loading, is studied.
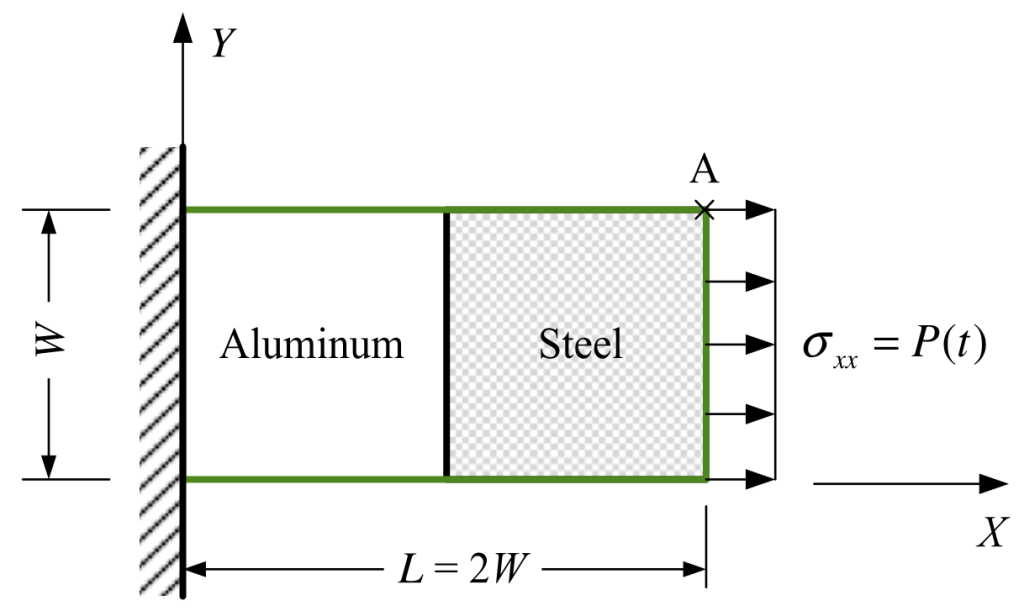
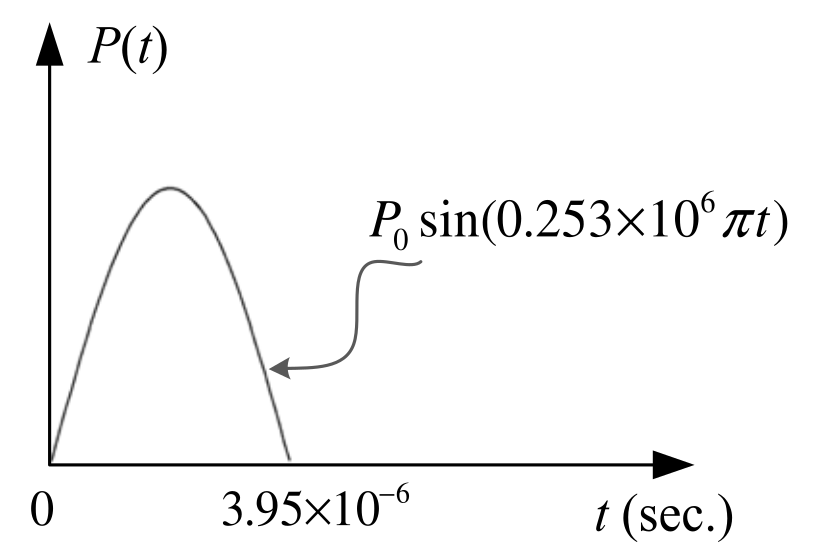
The plate is fixed at its left side, and traction free on its top and bottom sides, while the right side of the plate is subjected to a uniform tensile impulsive loading (solid_ic_bc.hpp). We have L = 50 mm, P0 = 100 MPa.
The domain consists of two materials: one half is steel and the other is aluminum. The material properties are: steel Young’s modulus E1 = 200 GPa, aluminum Young’s modulus E2 = 70 GPa, rho1 = 7860 kg/m3, rho2 = 2710 kg/m3, and the Poisson’s ratio of both parts is assumed null (nu1 = nu2 = 0) to impose 1D condition (props.txt).
Time step is 1e-8 s, with generalized alpha method using rho inf = 0.75 and zero acceleration (setup.txt).
The mesh has element size of 5e-4 m (mesh.geo).
Results for horizontal displacement at point A are reported below.
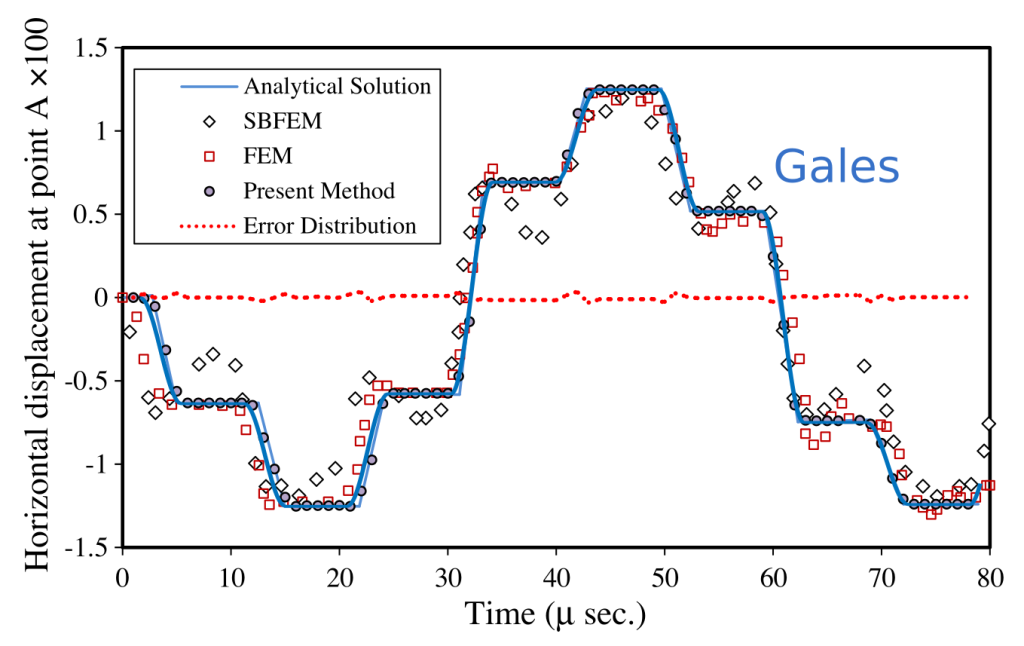
Reference
Khodakarami et al. “Modeling transient elastodynamic problems using a novel semi-analytical method yielding decoupled partial differential equations” (2012) CMAME
Proudly powered by WordPress
